1.0 Introduction
Digital Transformation is more than a buzzword; it’s a strategic imperative for organisations to remain competitive across all industries. It extends beyond just purchasing the latest technologies. Instead, it requires rethinking operation working practices – creating or changing processes, empowering employees, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation to deliver greater value to customers.
This article explores Digital Transformation by defining its core components, examining its benefits, and addressing the challenges organisations face on this transformative journey.
2.0 Defining ‘Digital Transformation’
2.1 Definition
“Digital Transformation is the continuous evolution of an organisation through the adoption and integration of new and improving technologies.“
Digital Transformation is about leveraging technology for ongoing, significant improvements in operations and customer value delivery. As technology evolves, organisations must also adapt to remain competitive.
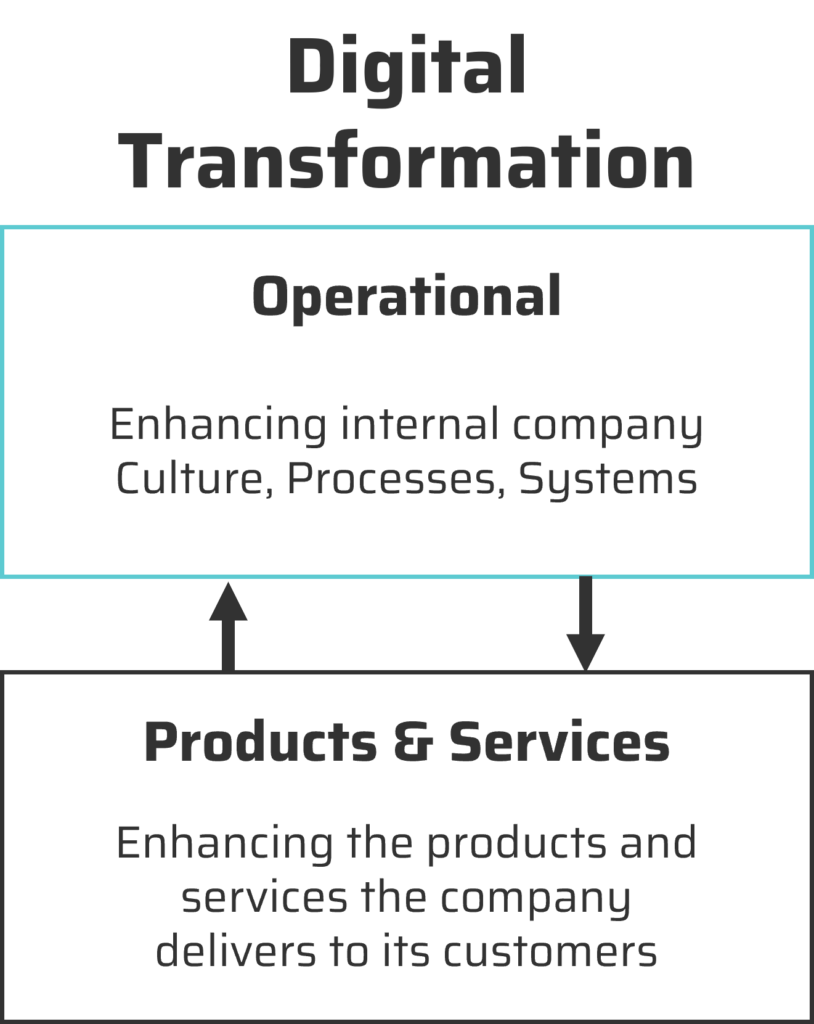
2.2 High-Level Types of Digital Transformation
Digital Transformation can be broadly categorised into:
- Operational Transformation: Using technology to enhance culture, processes, and systems.
- Product & Service Transformation: Leveraging technology to improve the products and services delivered to customers.
These categories can overlap; For example, adding connectivity to physical products can provide real-time data on performance, but this also requires changes in internal processes and cultural adaptation’. transforming ‘Services’ delivered to customers can be the result of Operational Transformation; for example, introducing a new Customer Feedback system.
2.3 When is an implementation classed as ‘Digital Transformation’?
Digital Transformation is often described as a journey, moving from A to B. Technically, any new technology adoption qualifies, however, the term is usually reserved for substantial, strategic changes.
Examples:
- Simple Adoption: Moving from paper to digital word processing.
- Complex Transformation: Deploying an enterprise-level CRM system.
While both examples could be classed as Digital Transformation, the latter represents a more significant, impactful shift. In industry, Digital Transformation typically refers to projects delivering measurable, long-term improvements in efficiency, agility, and competitiveness. It often involves major cultural, process, and operational changes, requiring comprehensive planning and resource investment.
2.4 The Benefits of Digital Transformation
If Digital Transformation offered no benefits, organisations would have little reason to embrace it. However, its impact has been undeniable across various industries. A couple of examples:
Ecommerce: Consider how eCommerce giants like Amazon have revolutionised the retail sector by leveraging digital tools to streamline supply chains, personalise customer experiences, and optimise operations.
Automotive: In the automotive industry, companies like Tesla are setting new benchmarks with connected vehicles, advanced manufacturing technologies, and over-the-air software updates.
These examples highlight how Digital Transformation drives innovation, improves efficiency, and positions businesses for sustained growth in a competitive landscape.
Every step of an organisation’s Digital Transformation journey should deliver one or more of the following benefits:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlines or automates operations and processes, saving time and resources.
- Improved Customer Experience: Delivers faster, more personalised, and seamless customer interactions.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Enables smarter, actionable business strategies with clearer data visibility across products, services, and operations.
- Innovation and Growth: Unlocks opportunities to create new products, services, or implement business models, or operational improvements.
- Collaboration: Strengthens communication and cooperation within teams and with external partners.
- Sustainability: Minimises waste by optimising resources and adopting eco-friendly practices.
- Competitive Advantage: Keeps the organisation ahead by embracing cutting-edge technologies.
- Adaptability and Future-Proofing: Ensures faster, more agile responses to market demands and technological advancements.
- Cost Optimisation: Reduces operational costs through efficient processes, smarter resource allocation. Reduces product costs through improved designs. In some cases, the “cost on paper” will increase – such as software licenses or increased infrastructure costs, as a side-effect of the tangible benefits of competitive advantages, better collaboration, sustainability…etc.
2.5 Drivers for Digital Transformation
Have you ever heard someone say, “We need to Digital Transformation our business,” or “Today, we start our Digital Transformation journey”? Probably not. Every organisation already uses digital technology in some form, whether it’s computers, internet access, or even fax machines, meaning they are already on this journey.
Digital Transformation often begins with identifying problems that need solving.
- Internal Innovation: Organisations may generate ideas internally, such as integrating new technologies to enhance operations, products, or services.
- External Factors: External influences, including evolving customer expectations, competitive pressures, industry standards, or regulatory requirements, can also drive the need for transformation.
At its core, Digital Transformation aims to enhance the profitability of an organisation either by increasing product or service sales or by improving operational efficiency; while this may sound obvious, the focus on measurable business impact and particularly return on investment (ROI) is often forgotten during the transformation journey.
3.0 Conclusion
Digital Transformation is not a one-time initiative but an ongoing journey requiring strategic alignment, cultural change, and a focus on leveraging technology to achieve measurable business outcomes.
To thrive in a rapidly changing digital world, organisations must continuously evolve – embracing new technologies, improving operations, and delivering greater value to customers. Ultimately, successful Digital Transformation creates a more agile, efficient, and customer-focused organisation, better-prepared to navigate future challenges and new opportunities.