Introduction
Digital transformation shapes every corner of engineering and manufacturing, implementing the "ecosystem" of core technologies is now essential for businesses to remain competitive and deliver value to their customers.
From product design to post-sale servicing, a diverse suite of systems supports efficiency, quality, and innovation.
This article explores key technologies and categorises them into functional domains, highlights their interdependencies, and defines each in plain terms.
Whether you're aligning IT infrastructure, mapping out a digital strategy, or onboarding team members, this guide offers a structured reference to help you navigate the digital landscape of modern industry.
Death by Acronyms...
The engineering and manufacturing sectors are saturated with acronyms- shorthand titles for complex systems and concepts.
Yes these Acronyms help condensing the content, but they create confusion and barriers for businesses and their stakeholders trying to learn digital transformation.
Before we proceed, see the table below showing the acronyms that exist for some typical Engineering and Manufacturing systems:
| Acronym | Full Title |
|---|---|
| ALM | Application Lifecycle Management |
| AR | Augmented Reality |
| BI | Business Intelligence |
| CAD | Computer-Aided Design |
| CAE | Computer-Aided Engineering |
| CAM | Computer-Aided Manufacturing |
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| CRM | Customer Relationship Management |
| ECAD | Electrical Computer-Aided Design |
| ERP | Enterprise Resource Planning |
| FEA | Finite Element Analysis |
| IDE | Integrated Development Environment |
| IIoT | Industrial Internet of Things |
| MCAD | Mechanical Computer-Aided Design |
| MES | Manufacturing Execution Systems |
| MRP | Material Requirements Planning |
| PDM | Product Data Management |
| PIM | Product Information Management |
| PLM | Product Lifecycle Management |
| QMS | Quality Management System |
| RMS | Requirements Management System |
| SLM | Service Lifecycle Management |
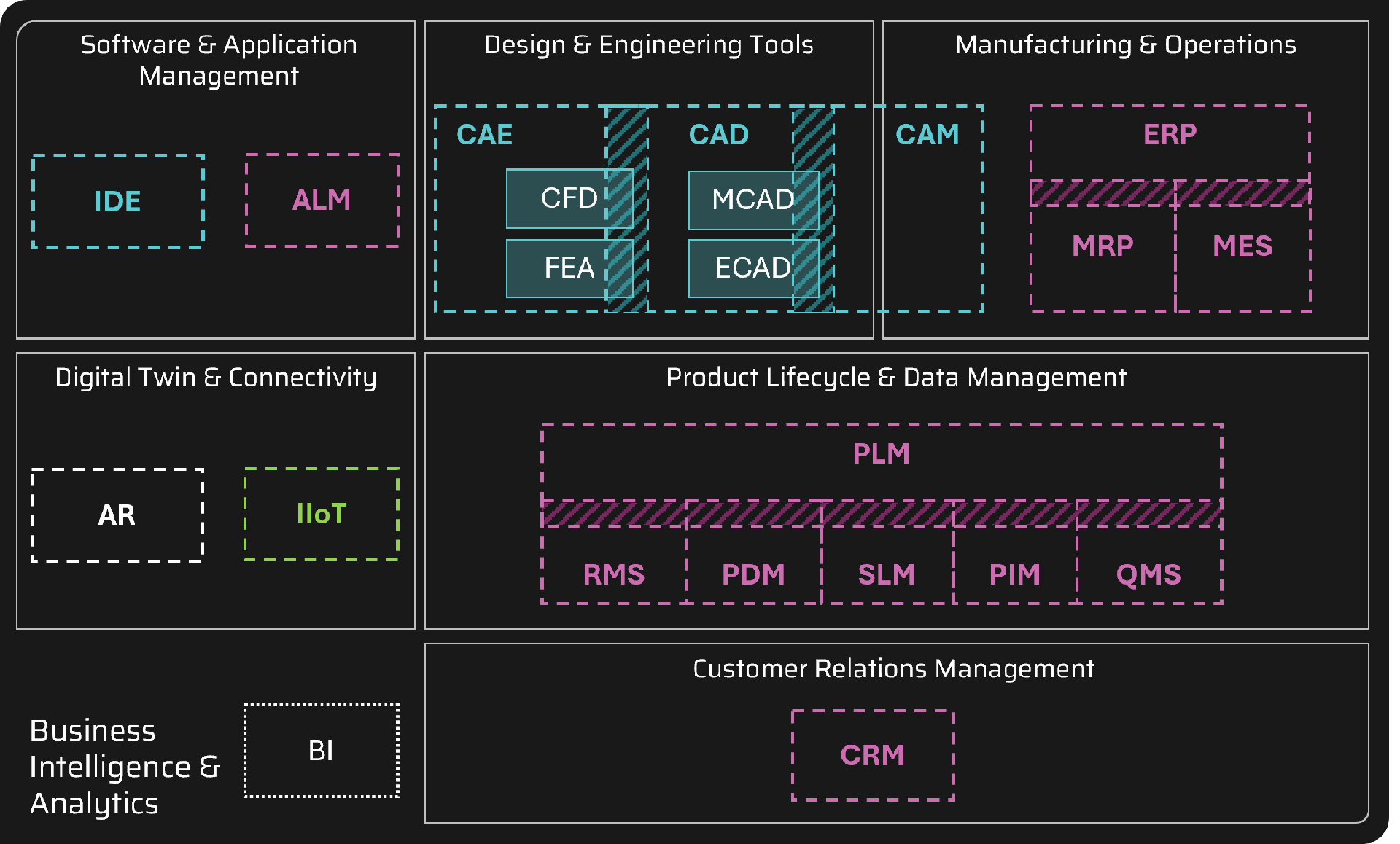
Application Categorisations
Functional Domains
We can categorise applications based on their functional domains to better understand their core purpose and role within the engineering and manufacturing value chain.
Functional Domains:
- Design & Engineering Tools
- Manufacturing & Operations
- Product Lifecycle & Data Management
- Digital Twin & Connectivity
- Customer Relations Management
- Business Intelligence & Analytics
- Software & Application Management

Functional Domain Architecture
When we categorise applications into this domains we will have overlaps between the domains, and also, the scope of the applications. This is because many modern tools are designed to integrate processes, support cross-functional workflows, and provide end-to-end traceability, reflecting the interconnected nature of digital transformation.
We also find that many modern applications have grown beyond their original scope, for example- ERP systems now have some MRP and MES capabilities, likewise with PLM systems which contain RMS, PDM, SLM, PIM, QMS, and more!
Types
Applications in engineering and manufacturing can be broadly categorised based on their primary function, which helps clarify their role within a digital ecosystem:
- Authoring Applications – These are tools used to create and modify digital content, such as CAD for mechanical design or ECAD for electrical schematics. They are essential for product development and design definition.
- Data Management Applications – These systems store, organise, and control access to data. PDM, PLM, and RMS fall into this category, supporting version control, traceability, and collaboration across teams. Some also support limited authoring (e.g. configuration rules or metadata).
- Visualisation Applications – Tools like BI or AR are primarily for presenting data in an interactive or digestible way. They help users interpret complex datasets or experience products virtually, without changing the underlying data.
- Authoring and Visualisation Applications – Some tools, especially IIoT platforms, serve dual roles. They not only visualise live industrial data but also allow users to configure dashboards, set alerts, or define logic, making them both interactive and generative.
Design & Engineering Tools
CAD (Computer-Aided Design): Software used to create, modify, and visualise detailed 2D or 3D models of products, structures, or parts.
Application Type: AUTHORING
CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering): A broad category of simulation tools that includes CAD, CFD, and FEA to evaluate and improve designs.
Application Type: AUTHORING
CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics): Simulation software used to model the behaviour of fluids (like air and water) and their interaction with solid surfaces.
Application Type: AUTHORING
MCAD (Mechanical Computer-Aided Design): A subset of CAD that focuses on the design, drafting, and visualisation of mechanical systems and components.
Application Type: AUTHORING
ECAD (Electrical Computer-Aided Design): Software used to design and document electrical circuits, schematics, and wiring diagrams for electronic systems.
Application Type: AUTHORING
FEA (Finite Element Analysis): Simulation software that evaluates how products react to physical forces like stress, heat, and vibration by breaking down models into finite elements.
Application Type: AUTHORING
Manufacturing & Operations
CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing): Software that converts CAD models into detailed instructions for machine tools and manufacturing processes.
Application Type: AUTHORING
MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems): Software that monitors and controls manufacturing processes on the shop floor, ensuring production efficiency and quality.
Application Type: DATA MANAGEMENT & AUTHORING
MRP (Material Requirements Planning): Systems that manage and plan inventory, materials, and production schedules to ensure efficient manufacturing processes.
Application Type: DATA MANAGEMENT & AUTHORING
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning): Integrated software systems that manage core business processes, such as inventory, order tracking, and manufacturing operations.
Application Type: DATA MANAGEMENT & AUTHORING
Product Lifecycle & Data Management
RMS (Requirements Management System): Software that captures, tracks, and manages product or project requirements throughout the development lifecycle, ensuring alignment with stakeholder needs and regulatory standards.
Application Type: DATA MANAGEMENT & AUTHORING
PDM (Product Data Management): Software that organises and manages design data, especially CAD files, to ensure accuracy, version control, and accessibility.
Application Type: DATA MANAGEMENT & AUTHORING
PIM (Product Information Management): Systems that centralise, manage, and distribute product-related information such as descriptions, pricing, and specifications across multiple channels.
Application Type: DATA MANAGEMENT & AUTHORING
PLM (Product Lifecycle Management): Software that manages a product’s entire lifecycle from initial concept through design, manufacturing, maintenance, and end-of-life.
Application Type: DATA MANAGEMENT & AUTHORING
QMS (Quality Management System): A system that ensures processes are followed to meet product quality standards and regulatory requirements.
Application Type: DATA MANAGEMENT & AUTHORING
SLM (Service Lifecycle Management): Software that manages a product’s maintenance, repair, and service operations throughout its lifecycle.
Application Type: DATA MANAGEMENT & AUTHORING
Digital Twin & Connectivity
AR (Augmented Reality): Technology that overlays digital content onto the real world, often used for training in manufacturing and service environments.
Application Type: DATA VISUALISATION
IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things): A network of connected industrial devices that collect and exchange data to optimise factory operations and product performance.
Application Type: DATA AUTHORING & VISUALISATION
Customer Relations Management
CRM (Customer Relations Management): A system that helps businesses manage interactions with customers, track sales, and gather feedback.
Application Type: DATA MANAGEMENT & AUTHORING
Business Intelligence & Analytics
BI (Business Intelligence): Software that analyses and visualises business data to support decision-making and strategic planning.
Application Type: DATA VISUALISATION
Software & Application Management
IDE (Integrated Development Environment): Software that provides developers with tools such as a code editor, compiler, debugger, and version control integration, all within a unified interface.
Application Type: AUTHORING
ALM (Application Lifecycle Management): A system that manages the entire lifecycle of software applications, from requirements gathering and development to testing and deployment.
Application Type: DATA MANAGEMENT & AUTHORING
